Polyline Export Statistics and Linear Quantity Takeoff Enhancements: CADPower-GeoTools V 17.15 Update
CADPower & GeoTools V 17.15 Update
Enhancement: CP_PL_STAT & GT_PL_STAT commands have been significantly enhanced.
CP_PL_STAT (CADPower-> Polyline Tools -> Inquiry Statistics -> Compute detailed polyline statistics):
GT_PL_STAT (GeoTools-> Polyline Tools -> Inquiry Statistics -> Compute detailed polyline statistics):
When working with 2d polylines with arc segments, three new fields have been introduced in the table output and CSV export.
They are ‘Arc Radius’, ‘Included Angle’ and ‘Direction’ (CW or CCW or ST).
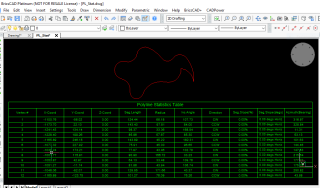
These three parameters are essential for CAD designers in the manufacturing industry, particularly machining operations, sheet metal fabricators etc.
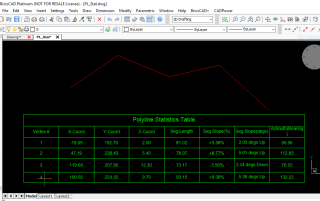
When working with 3d polylines, a number of bugs have been fixed and the polyline output is now significantly useful for surveyors etc.
Accurate segment distances and slopes are now computed and reported in the table as well as exported to CSV.
YouTube Video:
Enhancement: CP_LINEQTY (CADPower -> BOM/BOQ Tools -> Compute linear quantities):
The CP_LINEQTY command is used in association with the CP_DATAMAN command to compute linear quantities and report output like length, cost and weight. I have written about this command earlier, here and here.
This tool has been undergoing revisions and improvements regularly. We present the next set of improvements in this update.
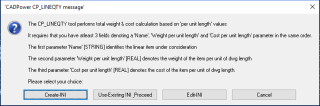
As you can see from the interface, it is now possible to create a template INI file from within the main dialog box.
The template INI file serves as a quick-start for your define your data definition to store the data with your linear entities.
The linear quantities tool (under BOM-Q) extracts cost and weight per unit length quantities from linear CAD objects. This tool has been improved.
You can now create a template INI file directly from within the CP_LINEQTY command itself.
The dialog box provides an option to create and edit an INI file from within the dialog itself.
The contents of the INI file are used more effectively now.
For example, this is an example of template INI file structure:
[*RECORD]
Name=LINE_INFO
Type=XDATA
FIELD=Name,String,Linear Part
FIELD=Weight per unit length,Real,1000.0
FIELD=Cost per unit length,Real,500.0
FIELD=Supplier,String,Linear Part Manufacturer
[*RECORD_END]
>> The name of the record is LINE_INFO, It can be used to describe your linear element, which can be a rebar, pipe, cable, duct
>> or casing etc.
>> The Type field is XDATA. Leave it as it is. It means that data is attached to entities as XDATA
>> The first 3 fields of the INI file are mandatory. The first field (in this example, ‘Name’) is used to identify the linear element
>> and can have any name.
>> The second field ‘Weight per unit length’ must be as it is and defines the weight per unit drawing length
>> The third field ‘Cost per unit length’ must be as it is and defines the weight per unit drawing length
>> The fourth parameter is optional and, if present, will be used to compute a table of quantities based on this parameter.
>> The fifth parameter is also optional and, if present, will be used to compute a table of quantities based on this parameter.
[*FIELD_VALUES]
Name=Name
Values=Type 1
Values=Type 2
Values=Type 3
[*FIELD_VALUES_END]
>> These are the different pre-defined values of the first parameter (in this case, it is called ‘Name’)
[*FIELD_VALUES]
Name=Weight per unit length
Values=100.0
Values=200.0
Values=300.0
[*FIELD_VALUES_END]
>> These are the different pre-defined values of the second parameter (called ‘Weight per unit length)
[*FIELD_VALUES]
Name=Cost per unit length
Values=1000.0
Values=2000.0
Values=3000.0
[*FIELD_VALUES_END]
>> These are the different pre-defined values of the third parameter (called ‘Cost per unit length)
[*FIELD_VALUES]
Name=Supplier
Values=Company 1
Values=Company 2
Values=Company 3
[*FIELD_VALUES_END]
>> These are the different pre-defined values of the fourth (optional) parameter (called ‘Supplier’)
[*SIZE_VALUES]
Name=Size
Values=Size 1
Values=Size 2
Values=Size 3
[*SIZE_VALUES_END]
>> These are the different pre-defined values of the fifth (optional) parameter (called ‘Size’)
You need to first attach data to linear entities like CIRCLE, LINE, ARC, POLYLINE, LWPOLYLINE or SPLINE objects.
This is done using the CP_DATAMAN command using the same INI file as above.
Once the data is attached, you can derive the linear quantities using the CP_LINEQTY command.
New CADPower videos added
CP_MOD_SHBL: CADPower, Blocks, Block-related, Globally Modify Block Properties
CP_BLKMAN: CADPower, Blocks, Block Names Editor
CP_POLYGETZ: Polyline Tools, Acquire Neighboring polyline elevations
GT_POLYINSVX @ GeoTools, Polyline Tools, Process, Polyline ‘Insert Vertex’ Tool
CP_PL_STAT: Detailed Polyline Statistics Now Shows Radius, Angle, Arc Direction in CADPower
CP_BOM: Counting the visibility states of a dynamic block in CADPower
New BricsCAD SupportTV videos
BRICSYS Support TV: How to show toolbars in BricsCAD
BRICSYS Support TV: Show/manage Commandline, Ribbons & Pull-Down Menus in BricsCAD
How to Create Lofted 3D Solids and Surfaces in BricsCAD
Cannot Save drawings: How to Fix this error in BricsCAD?
New GeoTools videos added
GT_POLYINSVX @ GeoTools, Polyline Tools, Process, Polyline ‘Insert Vertex’ Tool
GT_PL_STAT: Detailed Polyline Statistics Now Shows Radius, Angle, Arc Direction in CADPower
